
Plant Allergy Overview
Allergenicity
Moderate
Pollen Season
Spring
Type
Tree
Sub-Type
Deciduous
Allergy Information
Not particularly allergenic, hackberry could cause allergic reactions to those sensitized due to close proximity and continued exposure. Even though Celtis is in the same family as elm, a very allergenic genus, Celtis has not been found to be the source of a great deal of pollinosis.
Genus Details
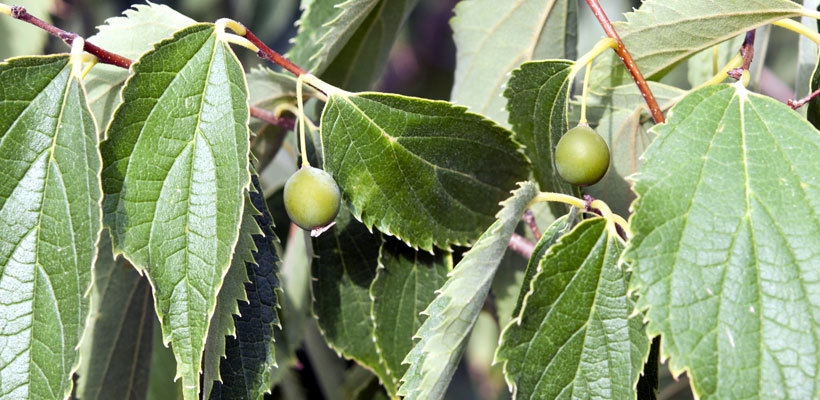
Hackberries are grown as shade and boulevard trees and shrubs in metro and rural areas. Trees can reach heights of 60 to 80 feet. Celtis has deciduous leaves that are alternate and simple. The fruit is a drupe, which contains a large seed and a thin, dryish, but sugary flesh (comparable to dates). The leaves of hackberry are similar to those of elms, but they are more pointed than elm leaves, and they are singly toothed along the edges.
Pollen Description
Grains are suboblate to spheroidal and are 3-10 porate. The sexine is thickened around the pores and granulate.
The pollen grains are typically 25-30 micrometers.
Genus Distribution
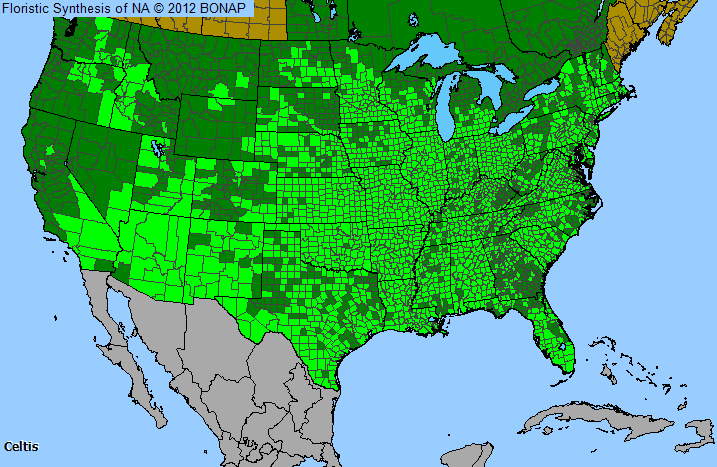
The shaded areas on the map indicates where the genus has been observed in the United States.
 - Native, observed in a county
- Native, observed in a county  - Introduced, observed in a county
- Introduced, observed in a county  - Rarely observed
- Rarely observedAllergens & Plants Search
Enter a full or partial species name to find more information on one of over 1,200 potentially allergenic plants.
For example, you can find chenopods searching on "cheno"

